TREATMENT
"Protect Your Manhood Get Informed About Penile Cancer-One Simple Check, One Big Difference Fight Testicular Cancer."

PENILE CANCER
Considered, like all other malignancies, a disease of the active cellular division from abnormal cells, which occurs generally in the penis tissue with the greatest frequency on the skin or in the foreskin. Today, it is an invasive malignancy but so rarely seen in the general population of men with an incidence of 0.4% w.r.t other known common cancers, which has been reported as associated with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection, the persistence of poor hygiene and tobacco abuse. They may consist of a lump or ulcer on the penis, bleeding or unusual excretions from the penis.
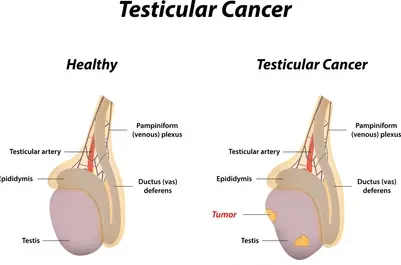
TESTICULAR CANCER
This type of cancer also affects the male reproductive organ’s cancer occurs in the testis which is found in the scrotum means an external pouch encasing stimulus. Men between the ages of fifteen to thirty-five are most likely to be inflicted with the disease. First July sight is a lump or bump in the testicle, or with more advanced disease, pain and swelling, or a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, lower abdomen, or groin.
SYMPTOMS OF PENILE CANCER:
- Bleeding or Discharge: Any unusual discharge from the penis, which however might be associated with bleeding, is one of the common signs.
- Changes in Skin Colour: Changes in colour, thickening or rashes on the penis are other signs and are often accompanied by nagging pain.
- Pain: Pain or tenderness of the penis occurs which is localized to the affected region.
- Swelling: There may also be swelling of the penis mainly at the tip.

SYMPTOMS OF TESTICULAR CANCER:
- Pain: Pain in the testis or scrotum or both either of dull or sharp quality. Other men, however, may have chronic soreness in the lower belly.
- Back Pain: In further stages, testicular cancer can cause back pain especially when the disease turns metastasis to the lymph nodes and other areas.
- Changes in Testicles Size: Distinct distortions in the dimensions, configuration or solidity of testicles.
- Heaviness in Scrotum: An inexplicable sense of weight or pulling in the scrotum.
PENILE CANCER TREATMENT

- Circumcision: They can proceed with circumcision in case the cancer is only limited to the foreskin.
- Excisional Surgery: It consists of the removal of the tumor as well as some normal healthy tissue around it. For some cases that are advanced total or partial removal of the penis (partial or total penectomy) will be required.
- Lymph Node Dissection: This may be performed if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, and thus, they have to be removed surgically.
- Radiation therapy can also be used as a primary treatment of the cancer or after surgery to kill any remaining tumor cells.
- To irradiate, for example, the patient may either use external beam radiation or brachytherapy (internalized radiation).
- Creams containing chemotherapy may be applied to the surface of the tumor for other stages of the disease.
- Where there is an advanced disease, and it is usually located in other sites than just the penis (systemic chemotherapy), the system is done via tablets or injections of the cancer drug.
- A therapy that enables the use of lasers in the destruction of cancer cells through the use of high-power light in most cases in the earlier stages of cancer.
- Cancer cells can also be killed by the use of cold-freezing balloons, also known as cryotherapy.
- The most common type of testicular cancer surgery is orchiectomy, a procedure performed to take out the affected testicle.
- In some patients, a surgical procedure termed RPLND is carried out to take out the lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity.
- It is often employed for localized seminomas or those that are confined to lymph nodes.
- The most common method used is external beam radiation.
- It can be administered in seminomas as well as non-seminomas, especially when there is an advanced disease out of the testicle.
- The regimen may involve combination chemotherapy using Cisplatin, Etoposide, and Bleomycin for several cycles.
- In early-stage testicular cancer, after surgery, surveillance (watchful waiting surveillance) is a therapy option that may be offered to the patients.
- This entails regular appointments with appropriate laboratory studies, imaging, and physical examination.
TESTICULAR CANCER TREATMENT

FOLLOW-UP CARE
- Follow-up is an essential component of any intervention to check for tumoral recurrence since treatment is done to avoid such.
- Diagnostic evaluation for follow-up care usually includes physical examination, tumor markers assay, and imaging.
