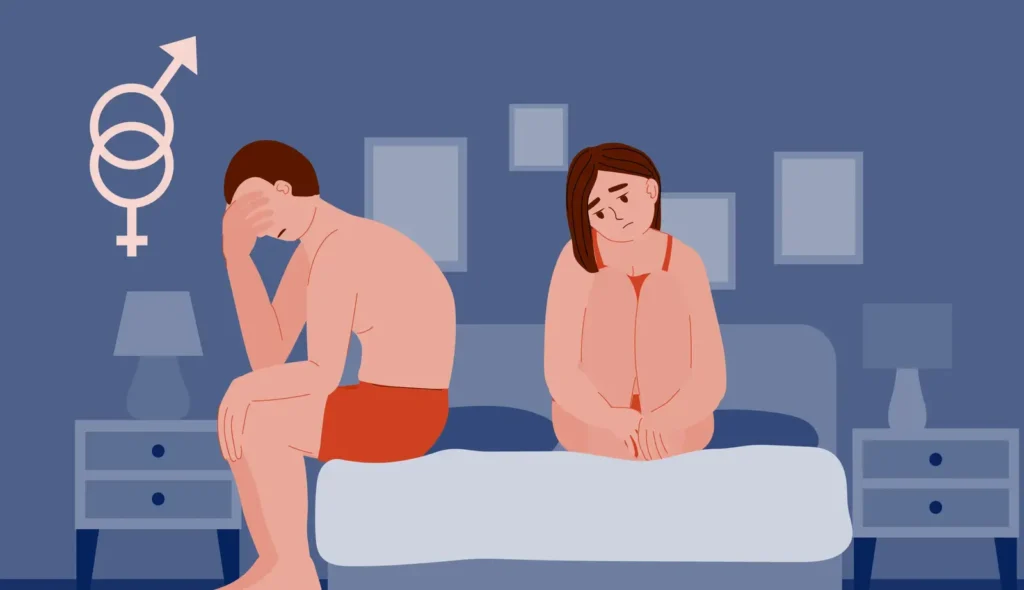
"Personalized Care for Your Sexual Well-being"
Sexual medicine can be defined as the subspecialty of urology that concerns itself with the clinical practice of diagnosing, treating, and managing sexual health for both males and females. This branch of medicine features a widespread variation of conditions that pertain to sexual function, procreation, and sexual health and well-being, as it comprises medical, psychological, and social dimensions to Board the patients. Therefore, Fertility urologists concentrate on problems that affect the patient’s quality of life and relationships or enhance self-confidence.
Key Areas of Focus in Sexual Medicine Practice in Urology
Erectile dysfunction remains the most sought-after sexual health issue needing attention in the practice of sexual medicine. The WHO IASP defines satellite dysfunction as the condition in which a man can achieve but cannot lose or hold a satisfactory penile erection long enough to permit satisfactory partnered sexual activity. Risk factors for ED include disease, mechanical phenomenon, endocrine and psychiatric disease conditions. Several tests including imaging, blood work, and psychological evaluation, among other tools are employed by urologists to establish the etiological agent of ED. Treatment options for ED include but are not limited to implantable penile devices ED vacuum devices and intracavernosal injections.
Premature ejaculation is yet another common concern that can greatly interfere with a man’s sexual pleasure and self-esteem. PE is mostly viewed as the quick firing which occurs at sex, particularly within a minute after penetration, and due to the poor control over the firing. Such treatment approaches in sexual medicine include a variety of behavioural therapies, some medications like Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), and the application of topical anaesthetics. There may also be a requirement for psychotherapy and sexual therapy if there are any psychological issues related to PE.
Hypogonadism also known as low testosterone is a disorder where the male body does not create enough of the male hormone testosterone and this hormone is required for sex, muscle, bone and even energy levels. Some of the symptoms may include low sex drive, inability to maintain an erection, lethargy, and mood swings. As regards sexual medicine, hypogonadism is diagnosed by urologists who perform blood tests aiming to gauge the sexual health of the patient and how the condition affects the overall health of the patient. Hormonal therapy or testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the most utilized method in returning normal hormone levels, functional sex performance and optimal life enhancement.
Although the name of this condition may make one think of the curvature of the penis in men. It should be noted that the del
embedded below from sources that cannot be cited Fundamentals of the Convex Dome Scultura content che consiste But what most of this negative language seems to imply o … When erect, the shaft of the penis shows a prominent curved shaft due to the formation of scar tissue, which makes it difficult or impossible during intercourse. With this curvature, painful erections, as well as penetration difficulties, and even impotence, are expected. When medical help is sought, the US plans a range of sexual devices to treat Peyronie’s disease mainly involving therapy with a cast without surgery. A urologist is also an important healer who gives psychological help to patients suffering from psychological problems related to the illness.
If there is one area of the sexual medicine menu that has long been associated with men’s health it would be hypersexuality. Besides problems that patients face female sexual health has also been targeted with female arousal disorder including HSDD, lack of lubrication, and dyspareunia. Some urologists engrossed with sexual function have female patients and are interested in aetiology such as hormonal factors associated with menopause, urogenital pain syndromes, or mental health issues. HRT, lubrication, pelvic floor rehabilitation, and psychological therapy may be provided.
After Surgery In most cases, the sexologist tends to the sexual rehabilitation of patients who for one reason or another have undergone some of the surgeries that affect sexual function, for instance, prostatectomy, cystectomy, or pelvic cancer surgery. Urologists design individual rehabilitation programs for the patients which may comprise medication, penile rehabilitation techniques, vacuum apparatuses and psychological fortitude to enhance the return of sexual function and libido.

Types of Sexual Dysfunction
Sexual dysfunction encompasses a variety of disorders occurring at some point in the sexual response cycle and preventing individuals or couples from obtaining pleasure from any sexual activity. It can be seen in both men and women and can be attributed either to biological reasons, psychological or both.
For Men:
Inability to develop or sustain an erection adequate for penetration.
An instance of ejaculation occurring earlier than desired in the course of sexual intercourse.
The inability of a man to ejaculate despite good stimulation and or penetration from the woman’s vagina.
Decreased or lack of desire to initiate or engage in sexual activities for both genders.
For Women:
Difficulty in becoming sexually excited or sustaining arousal at any time during intercourse.
Reaching orgasm is often fatiguing and may take long to accomplish in women; this is known as delayed orgasm.
Painful intercourse due to different kinds of factors whether physical or psychological.
The interest or desire to perform sexual acts is missed in women.
Psychological Causes:
Stress, Anxiety, and Depression:
All of these body disorders can flush out sex drive from circulation.
Relationship Issues:
Miscommunication, anger, and lack of faith can all cause issues for a woman sexually.
Trauma:
A portion of the population has a history of sexual trauma which affects their sexual wellbeing.
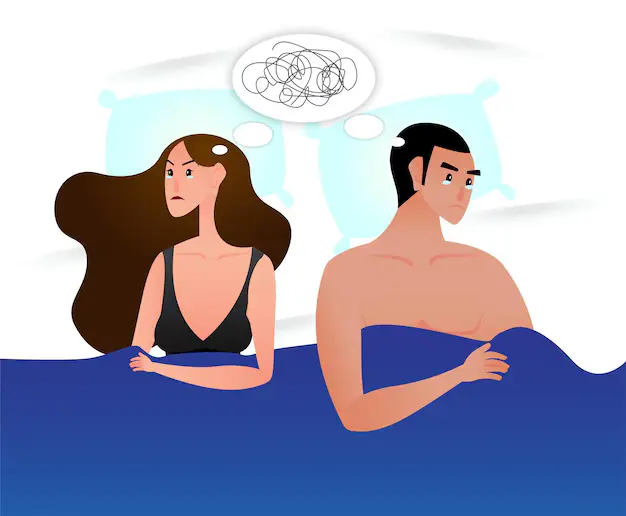


Treatment Options
Medications
Psychological Counseling
Relationship Counseling
Surgical Options
Considerable within sexual medicine in urology is the recognition that sexual health is an integral component of the entire health and as a result, a comprehensive viewpoint is taken towards the patients. Many urologists do not work alone but in need of other specialties such as endocrinologists, psychologists and sex therapists, to provide comprehensive treatment of all sexual health and its related disorders.

