Empowering Recovery, Defeating Adrenal Gland Tumors.
Adrenal tumors: Know the signs.
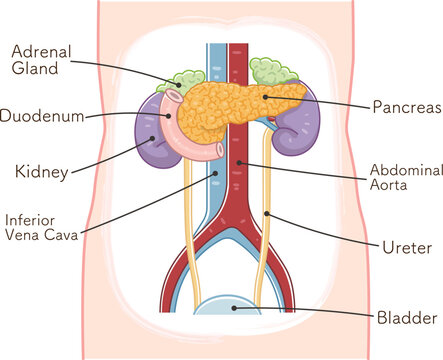
Adrenal gland tumors are lumps or masses that appear in the adrenal glands, which are positioned on top of the kidneys. Depending on the situation, these tumors can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). The treatment for adrenal tumors depends on several factors, such as the type of adrenal tumor, whether it is functional or non-functional, and if it is benign or malignant.
Types of Adrenal Tumors
Adrenal Adenomas: This type of tumor is an adenoma and is obnoxious, meaning that it will usually not secrete any excess hormones. However, a few will secrete hormones leading to Cushing syndrome or Conn’s syndrome, respectively.
Adrenocortical Carcinomas: a sporadic form of cancer that is malignant and sometimes secreting hormones and also can metastasize to other body tissues.
Pheochromocytomas: tumors found in the adrenal medulla that cause secretion of excessive catecholamines, leading to symptoms like hypertension.
Metastatic Tumors: Tumors found in adrenal glands as a result of migration from some other tissue sites in the body.
Treatment Options for Adrenal Tumors:
Surgery (Adrenalectomy)
Indications: In most cases, surgery is the primary treatment option for adrenal tumors, mainly if they are significantly symptomatic and if there is endocrine abnormality secondary to adrenal tumors.
Types of Surgery
Medications
Radiation Therapy
This treatment is used less frequently, but it can also be used in the management of malignant adrenal tumors when surgery cannot be performed or where there is a risk of recurrence post-surgery.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
It is a procedure that destroys small tumors by means of heat and is carried out with minimal invasion. It is possible to offer this option to patients who otherwise are not surgical candidates.
Observation:
All the evidence regarding a small, non-functional, and peripheral adrenal tumor is pain; it may be reasonable even to adopt a “wait and watch” strategy based on routine follow-up. This includes frequent examinations with imaging techniques to prevent animals from growing or becoming active.
Post-Treatment Considerations
Supportive Care
Some impairment in personal functioning may warrant psychological support and counseling, especially if it is due to treatment therapy or if the tumor is malignant.
Recovery may also include nutritional and physical rehabilitation therapy.
Early diagnosis and personalized medicine are essential for the effective management of adrenal tumors, however, there is a need for regular follow-up for the overall health and well-being.